News

The Global Trade and Sustainable Future of Plastic Bags
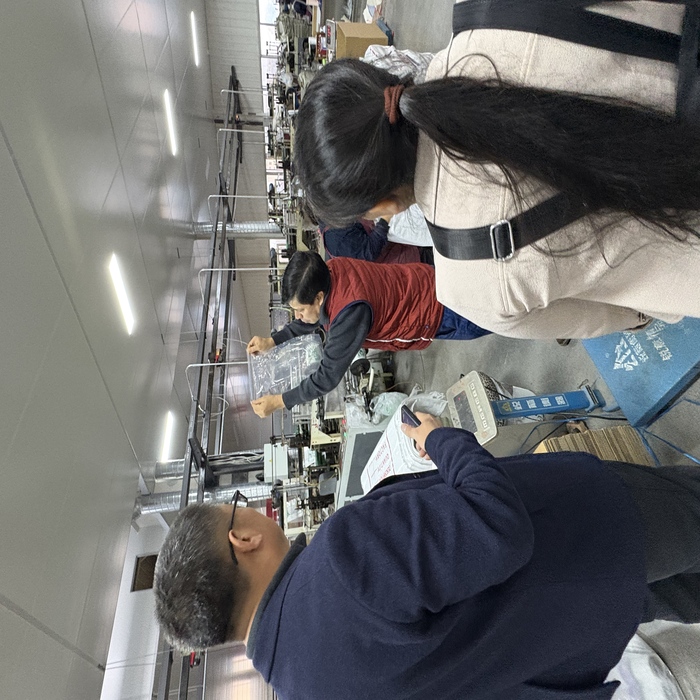
Plastic Bags, as an essential packaging material in modern life, are closely tied to the development of international trade. With the acceleration of globalization, the demand for plastic bags in foreign trade continues to grow, particularly in consumer goods, food packaging, and other sectors. However, environmental concerns and shifting international trade policies also pose challenges for the industry. This article explores the current state of global trade in plastic bags, market drivers, environmental pressures, and future trends, analyzing their role in the global economy and pathways for sustainable transformation.

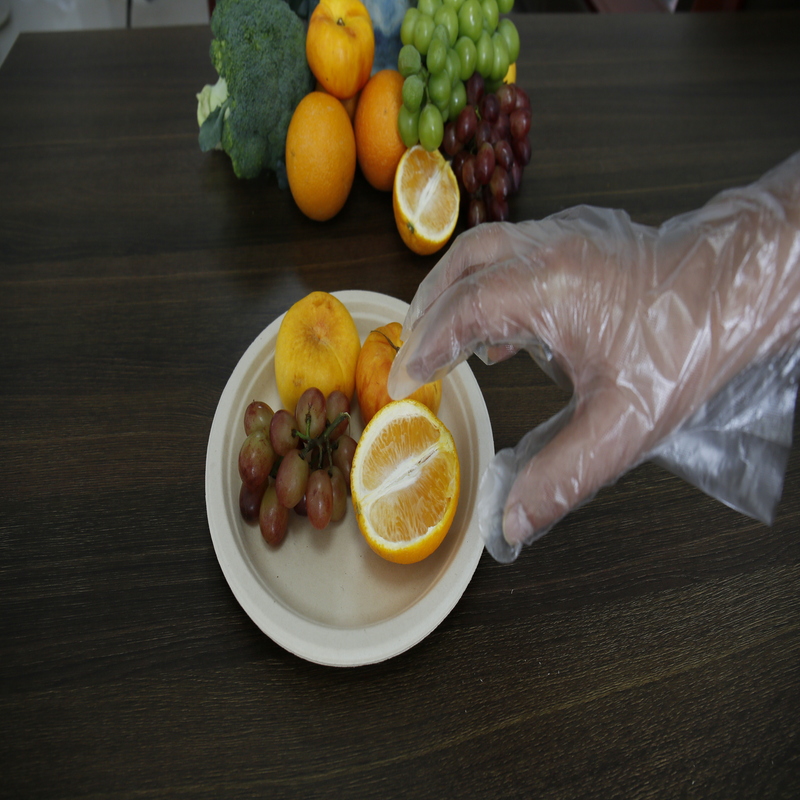
A Comprehensive Guide to Garbage Bags: From Selection to Eco-Friendly Use
Garbage Bags have become an indispensable cleaning product in modern life, widely used in households, offices, property management, and commercial spaces. Their existence has greatly facilitated waste collection and disposal, making environmental sanitation management more efficient. However, faced with the wide variety of garbage bag products on the market, many consumers often feel confused when making purchases. This article will provide a comprehensive guide covering the types, materials, selection techniques, usage considerations, and environmental trends of garbage bags.

The Underrated Benefits of Plastic Bags: A Reassessment of Their Role in Modern Society-1
Plastic bags, often vilified in contemporary environmental discourse, have become a symbol of humanity’s struggle with waste and pollution. Images of floating garbage patches in oceans and entangled wildlife dominate headlines, fueling calls for bans and restrictions. However, this one-sided narrative overlooks the multifaceted advantages plastic bags have offered since their widespread adoption in the mid-20th century. This article aims to provide a balanced perspective by exploring the economic, practical, and even environmental benefits of plastic bags, arguing that their utility should not be dismissed without acknowledging their contributions to human progress.
What is copolymer polyoxymethylene? What are its applications?
Copolymer polyoxymethylene (also known as polyoxymethylene copolymer or polyoxymethylene copolymer) is a high-performance engineering plastic. In addition to repeated -(CH₂O)- segments in the main chain of its molecule, it also contains other copolymer monomer segments (such as ethylene oxide, dioxolane, etc.). Its molecular weight is usually between 20,000 and 40,000. It has excellent comprehensive properties, such as high mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, creep resistance, low friction coefficient, chemical corrosion resistance, etc. It is called "super steel" or "steel", and can partially replace metal materials such as copper, aluminum, and zinc.
World's First "Reed-to-Plastic" Production Line Begins Operation, Capable of Producing Polylactic Acid
Recently, the world's first polylactic acid (PLA) production line using reeds as raw material officially commenced operations. The facility consumes approximately 50 tons of reeds, straw, and other raw materials daily, producing around 10 tons of PLA and lignin. This production line was invested in and constructed by a Chinese company, whose independently developed production technology is internationally leading, successfully filling the gap in non-food-based bioplastics.

Understanding All Six Polyethylene Modification Methods
LDPE typically has a crystallinity of 55–65%, while HDPE ranges from 80–90%. Although PE possesses excellent mechanical processing properties, its inert and non-polar surface results in poor printability, dyeability, hydrophilicity, adhesion, antistatic properties, and compatibility with polar polymers and inorganic fillers. Additionally, its wear resistance, chemical resistance, environmental stress crack resistance, and heat resistance are limited, restricting its application scope. Modification methods are employed to enhance its performance and expand its applications.

AirAsia Adopts Polylactic Acid (PLA) Tableware
April 21, 2025 – Santan, the food and beverage division of Capital A (formerly AirAsia Group), has announced its shift from single-use plastics to biodegradable alternatives, marking a significant step in reducing its environmental footprint. All disposable items onboard, including cups, lids, and cutlery, will now be made from polylactic acid (PLA)—a material derived from renewable resources such as corn and cassava.
Developed by Rightway New Material, PLA offers key advantages over conventional plastics, decomposing at a m

Flame-Retardant ABS
ABS is a flammable material, classified as HB level according to the UL94 standard. When ignited, ABS burns rapidly, releasing large amounts of toxic gases and black smoke, making it unsuitable for many practical applications. With advancements in technology and improvements in quality of life, safety awareness has grown significantly. Both domestic and international industries have imposed strict fire safety and flame-retardant requirements on plastic materials used in automobiles, construction, home appliances, office equipment, and other fields, accompanied by corresponding technical standards and regulations. Therefore, research on flame-retardant ABS holds considerable importance.
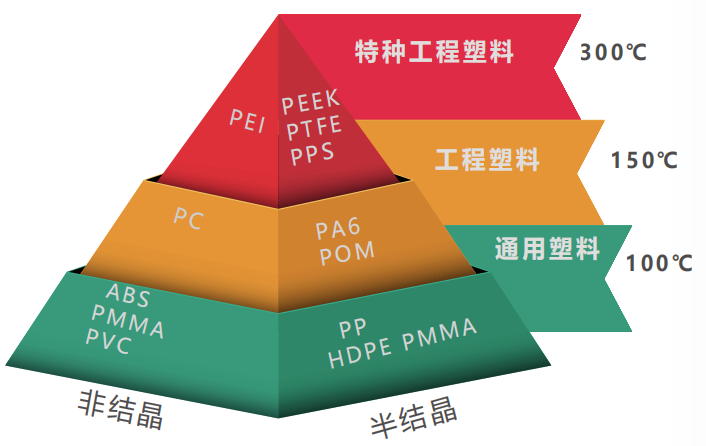
Classification of plastic
There are numerous types of plastics (e.g., PE, PP, PVC), widely used in packaging, construction, healthcare, automotive and other fields, meeting both daily and industrial needs.
Methods for Modifying PET
When PET is blended with PP, the resulting alloy combines the advantages of both, enhancing overall performance. For example, PET improves PP's heat resistance, while PP reduces PET's moisture sensitivity. However, without a compatibilizer, PET/PP blends exhibit weak interfacial adhesion and poor mechanical properties.